WHAT IS THE PEG RATIO?
In case you have never come across this quaint, and potentially dangerous, little valuation shortcut, let me provide a brief overview. The PEG ratio compares the price to earnings (P/E) ratio of a business to its expected future growth rate (G); this period is typically five years.
P/E ÷ G = PEG ratio.
Sometimes you will see a P/E ratio in the calculation that utilizes next year’s expected earnings, rather than the more typical version that uses the company’s current P/E.
The supposed wisdom behind the PEG ratio says that a P/E ratio, even a forward-looking one, only accounts for the grow
th in an earnings stream one year out. By incorporating the company’s expected growth rate for a longer period of time, like five years, you supposedly get greater insight into whether or not it makes sense to buy stock in a company. Just like a P/E ratio, the lower the PEG ratio is, supposedly the less expensive is the stock.
SHOULD I TRUST THE PEG RATIO?
Importantly, does the PEG ratio have any basis in reality and can you trust it? To both questions the answer is: sort of, but not really. In evaluating these answers, believe it or not, no subjectivity is necessary. How can that be?
PEG ratios are actually based on mathematics. Shockingly, the PEG ratio is only accurate under a very specific set of circumstances that are rarely ever met in the investment market place.
Because almost all of us know and love Apple as a business – if not necessarily as a stock – I am going to use it as an example to illustrate my points.
As of the close February 17, 2011 shares in technology juggernaut Apple are selling for $358.30. Compared to trailing earnings per share of $17.92, those two figures give us a P/E of:
$358.30 ÷ $17.92 = 19.99x
Yahoo! Finance reports that Apple’s five year expected growth rate (G) in earnings is 26.3%. So, in turn, that gives us an Apple PEG ratio of:
19.99x ÷ 26.3% = 0.76
[Note: if you actually crank out this math you know that you don’t really get 0.76. That’s because the growth rate is not treated as 0.263 (or 26.3%), but as 26.3 for the PEG ratio calculation.]
Okay, so now that we have our PEG ratio, 0.76, what does it mean? Traditionally, if your PEG ratio is greater than 1.0 it means that the business you are looking at is overvalued and that you shouldn’t buy that company’s stock unless you feel that the growth rate, G, used to calculate the PEG ratio, is too low.
Conversely, if the PEG ratio is less than 1.0 it means that a business is fairly valued, and in fact, trading at a discount. Such a purchase is done with a classic Graham and Dodd, value investing, margin of safety it is said. A PEG ratio of approximately 1.0 supposedly is an indication of fair value.
So if I were to invest in Apple using the traditional understanding of the PEG ratio I would normally conclude that shares in the business are cheap; actually, not just cheap, but super cheap. Shares in AAPL are trading at a:
( 0.76 PEG ÷ 1.0 PEG ) – 1 = 24.0% discount to fair value
WOW! Apple looks like a steal. But here is where we bump up against my point: the fallacy of the PEG ratio as a valuation measure. Someone trusting this rule of thumb valuation measure has the potential of really being stung. Here’s why.
An investor buying Apple at the 0.76x PEG ratio would be sadly disappointed to learn that he would only end up with a 8.9% compound annual growth rate at the end of five years. This assumes that the 19.99x multiple paid holds flat (i.e. the return of capital at the end is the same as put in), but that Apple does, in fact, deliver average annual earnings growth of 26.3%.
The above result is mathematically derived; the only subjectivity is in my assumptions – that is, does Apple deliver those earnings, and does its P/E multiple stay flat? And I am being generous with my assumptions, too. I am assuming that you, as an investor, would be happy with a 0.0% rate of return. In other words, I’m not factoring in your expectations for return in this calculation. Normally investors should factor in their return expectations – their required return – when evaluating investments.
What happens if I factor in a five year expected rate of return on my part of just 10%? Well then the return for Apple drops to 6.7%. Okay, you might say, this is surprising, but Apple will take its earnings and reinvest them in the business and earn high rates of return on that re-invested capital.
Let’s assume then that Apple does pump all of its retained earnings back into innovative, juicy products like the iPod, iPhone and iPad and that it continues to earn 26.3% on those new products. Even in this scenario, Apple just meets the breakeven required rate of return, delivering a 10% compound annual return.
Correct me if I am wrong, but I think that when most people invest in a business like Apple they are expecting their return to be the same as the company earnings growth – in Apple’s case, that’s our familiar 26.3%. But instead, we need aggressive assumptions just to get to a 10.0% rate of return even though Apple’s PEG ratio is 0.76. And this demonstrates the fallacy of the PEG ratio.
So how is it that the PEG ratio breaks down?
Here is a list of the principle PEG ratio problems to be aware of, as revealed by mathematics:
1. The PEG ratio doesn’t account for the time value of money. That is, when you invest $358.30 in Apple in exchange for just $17.92 of earnings, those earnings have to grow rapidly – in fact, more rapidly than the expected earnings growth rate of 26.3% – for you to earn your required return.
2. The PEG ratio makes no assumption for how the business or you reinvest earnings. And even when you factor this in to your calculations, you still need much more massive earnings growth than the PEG ratio would imply you need, again due to the time value of money.
3. The PEG ratio doesn’t factor in your investment time horizon unless you were careful in using an earnings growth rate commensurate to your preferred time horizon. In the above examples with Apple under the microscope I assumed five years. But if your investment time horizon is just 3 years, then in the aggressive case Apple only returns 7.7%. By contrast, a time horizon of 10 years generates a compound annual growth rate of 15.4%. However, most businesses cannot grow their earnings at such high rates of return (26.3%) for a decade, especially when they are beginning at an earnings base in the billions, as is Apple.
4. Very importantly, the PEG ratio treats all 0.76x ratios as being the same, when in fact they are very different. For example, Apple’s PEG ratio of 0.76 is a combination of a P/E of 19.99x and a growth rate of 26.3%. Recall that in the baseline case this resulted in a 8.9% annual return. But what if instead that 0.76 PEG were achieved by:
9.995x P/E (exactly half of Apple’s) ÷ 13.15% Growth rate (again, exactly half) = 0.76 PEG ratio
The results are actually dramatically different. In this case the average annual five year return is 11.7%, not the 8.9% of Apple’s 0.76x PEG ratio!
Likewise, a PEG ratio where Apple’s P/E and Growth rates are doubled, 39.98x and 52.6%, respectively, also provides a dramatically different result. Here the compound annual return is 8.8%. While comparable to Apple’s actual expected compound annual return of 8.9%, remember that an investor buying at a PEG of 0.76x where the five year growth rate in earnings is expected to be 52.6% will be sorely disappointed.
The culprit again is the time value of money. A P/E of 39.98x means that you are trading $39.98 for $1 of earnings. This is an exchange that you wouldn’t likely make at a Las Vegas casino. So that $1 of earnings has to grow very, very fast to make up for the disparity in what you paid at the outset to what you receive over the intervening years.
WHEN DOES THE PEG RATIO HOLD UP?
So in what very special case do you actually earn the same rate of return that the company does? That is, if I buy Apple shares wanting my rate of return to equal Apple’s 26.3% earnings growth rate, how do I do that?
Unfortunately, the traditional PEG ratio heuristic of “companies are a value when the PEG ratio is less than 1.0x” focuses your attention incorrectly – it is close, but no cigar.
The two things you want to focus on are:
1. All three rates of return involved in the investment are identical, and without any deviation. These three returns are:
- The company’s earnings growth rate
- The rate of return on reinvested earnings
- Your required rate of return on the investment
2. The unified rates of return, from just above, when multiplied by the P/E, must total 1.0.
An example will help to make this clear. If you pay a 20x P/E then fair value is when the company’s earnings growth rate, the rate of return on reinvested earnings, and your required rate of return all equal 5.0%. That is, fair value occurs here because 20 x 5% = 1.0. If these very special conditions are met, then your actual compound annual return will be identical to the three flows above, or 5.0%.
Likewise, if you pay a 30x P/E then the three rates of return must all be 3.33% (30 x 3.33% = 1.0). If this is the case, then your return will be 3.33%. When these stars all align then your investment time horizon is irrelevant because this result holds for all investment time horizons.
Very importantly, the PEG ratios for these two scenarios are very different even though they both are scenarios where the stock is fairly valued. In the 20x case, the PEG ratio is 4.0x (= 20x P/E ÷ 5% Growth); whereas in the 30x case, the PEG ratio is 9.01x. So we have fair value with a PEG ratio of 4.0x and also at 9.01x. This clearly violates the “fair value is when the PEG is 1.0x” rule of thumb.
Another way of stating all of this is: a business is fairly valued when all of the rates of return are all equal to the earnings yield of the business. The earnings yield is simply the inverse of the P/E ratio. So a 20.0x P/E business has an earnings yield of:
1 ÷ 20.0x = 5.0%
We saw above that when all of the rates of return for the 20.0x business were all 5%, that is equal to the earnings yield, that the business was fairly valued.
So there is one, and only one, very special case in which the PEG ratio heuristic of “a 1.0x PEG ratio indicates fair value” holds up. That is when the rates of return are all 10.0% and the P/E paid is 10.0x. Here you have a PEG ratio of 1.0x, rates of return of 10% and the result is that you get exactly what you paid for: a 10% compound return. May you be so lucky to experience such a convergence.
It seems to me that somewhere in the deep, dark past of investing that the communication of the significance of the PEG ratio went awry. Does it make sense to compare the P/E to the earnings growth rate? Absolutely. Does the number 1.0 hold a special significance when using the PEG ratio? Absolutely. But on this latter point the focus is messed up. The 1.0 part of the relationship is that the P/E multiplied times the unified growth rate must equal 1.0; when this is the case there is fair value.
WHEN IS THE PEG RATIO DANGEROUS?
It should be obvious that the PEG ratio is dangerous almost always! It implies to the naïve investor that a business is a value when it is trading at less than a 1.0x PEG ratio. But this is patently false.
Standard interpretations of PEG ratios also imply that you will receive the same rate of return on your investment as the company you have invested in makes on their earnings. This is also patently false.
I have also demonstrated that PEG ratios just are not comparable. A 0.76x PEG ratio is not the same across situations. A company with a high P/E is especially dangerous when using the PEG ratio as an indication of value because the rates of return are much lower than implied by earnings growth rates.
WHAT DO I ADVISE?
I don’t advocate an abandonment of the thinking behind the PEG ratio, where the price you pay is compared to both current earnings and the growth rate in earnings. But I do advocate that you understand just what it is you are looking at when you use a PEG ratio.
So here are the new rules of thumb for PEG ratios (because, don’t you know, it’s slightly more complicated than this; however, these do hold much, much better than the traditional use of the PEG ratio as a valuation metric):
- A business is overvalued when the flows associated with it – its earnings growth rate and the reinvestment rate of its earnings – are less than its earnings yield and your required rate of return. For example, with a 20.0x P/E stock (like Apple), its earnings yield is 5.0% (1 / 20x P/E). If either the earnings growth or reinvestment rate is less than 5.0% then you are overpaying. But the business is also overvalued if your required rate of return is higher than both the earnings yield and the returns generated by the business. Thus, if your required return is 6.0% for a 20.0x P/E stock, paying 5% and reinvesting at 5%, then you are overpaying.
- A business is undervalued when the opposite above is true. So if the rates of return associated with the business are greater than the earnings yield then you are looking at an undervalued business. For the 20.0x, earnings yield of 5% business, if the rates of return are 6.0% then the stock is undervalued. This assumes of course that your expected rate of return is lower than, or equal to, the earnings yield of the business. To make money beyond your expectations your required rate of return has to be 5% or less.
WHAT ABOUT APPLE? IS IT A BUY OR A SELL?
The biggest assumption about Apple, from a PEG ratio standpoint, is what is your required rate of return? For me personally, if I am going to risk my capital in the stock market I want at least a 10.0% rate of return.
The next big assumption for Apple is what kind of average rate of return do I feel it will earn on its reinvested earnings over the next five years? My own thought is that, as inventive as Apple is, that it will be many years until its next iPod, iPhone and iPad is created. The reason is that these devices revolutionized the primary electronic devices already in our lives. That is, how we listened to music, how we placed phone calls, and how we compute.
What other electronic devices are there to revolutionize? You could argue video games. But Apple has not indicated a willingness to enter into the video game space against the entrenched giants. It may do so, and it may do well, but I think it is unrealistic to expect that the reinvested earnings will grow at that 26.3% level. So I am going to assume that reinvested earnings grow at 20.0%.
My investment time horizon is five years – because that’s just how I roll. When I crank out the return numbers for Apple, even at its 0.76 PEG ratio, I get a compound annual return of 9.1%. Not bad, but less than my required rate of return of 10.0%. So Apple looks slightly overvalued to me.
The critical assumption here is actually the reinvestment rate of earnings. In order for Apple to be fairly valued, while expecting a 10.0% return over 5 years, then the reinvestment rate of earnings needs to be at least…get ready for it…26.4%. In other words, to do better than a 10.0% average annual return I have to bet that Apple’s earnings will grow faster than even Apple and its analysts foresee. And I am not a betting man, I am an investor.


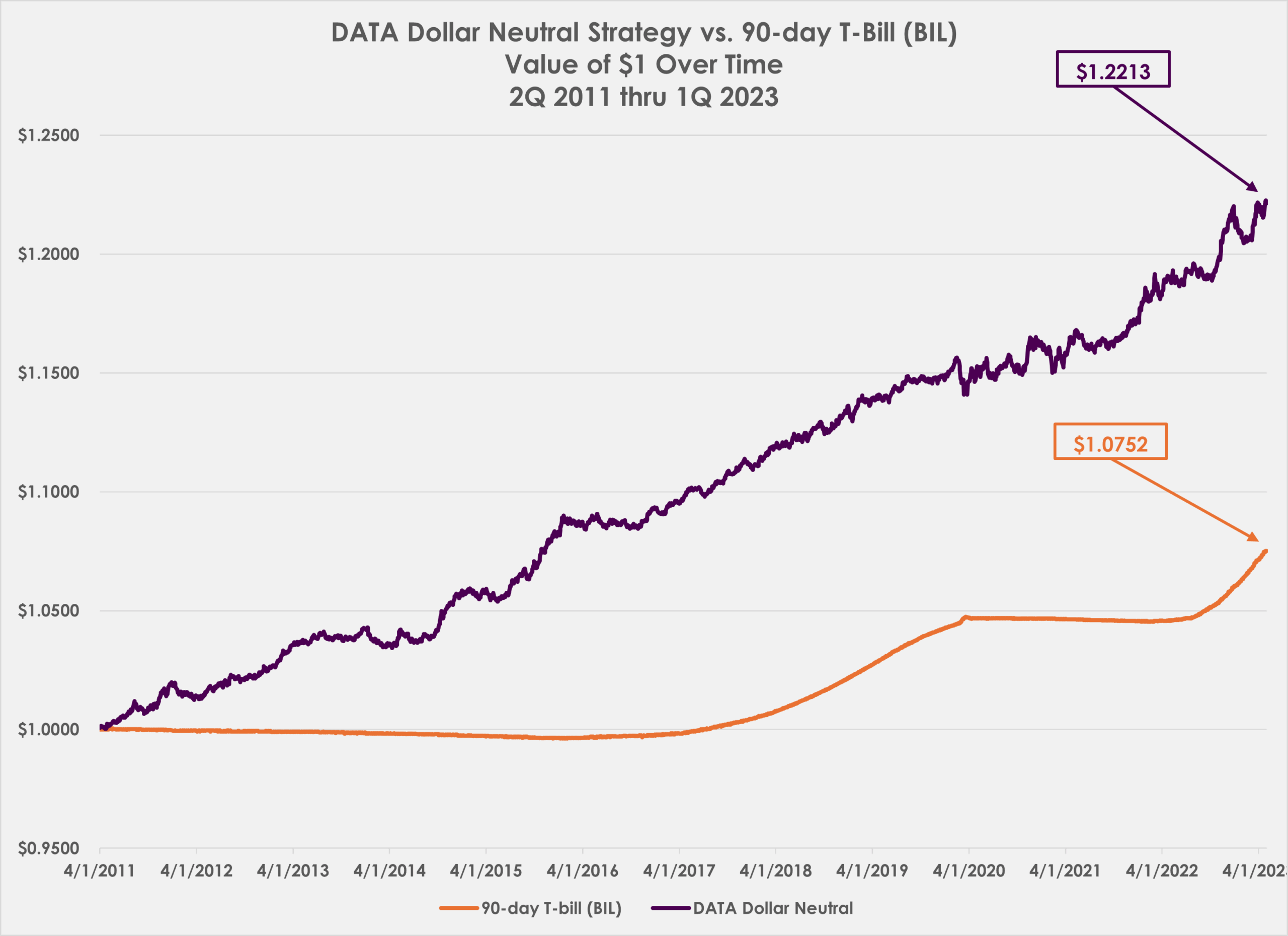
I disagree with on:
“An investor buying Apple at the 0.76x PEG ratio would be sadly disappointed to learn that he would only end up with a 8.9% compound annual growth rate at the end of five years. This assumes that the 19.99x multiple holds flat, but that Apple does, in fact, deliver average annual earnings growth of 26.3%.”
– If P/E holds flat and earnings grow at 26.3%, the price must also grow at 26.3% o.w P/E would change.
Hi Stefan,
You are correct. What I meant to say was, “This assumes that the 19.99x multiple paid holds flat…” In other words, the return of capital at the end, is the same as was put in. In other words, there is no multiple expansion.
Sorry for the confusion and I will amend the posting.
Jason